objective Ques (161 results)
SSC CGL 202041)ABC is an equilateral triangle. P, Q and R are the midpoints of sides AB, BC and CA, respectively. If the length of the side of the triangle ABC is 8 cm, then the area of \(\triangle PQR\) is:
\({4\sqrt3}\space cm^2\)
In the\(\triangle ABC\), point P, Q, R are mid points so,
Sides of the \(\triangle PQR\) = 8/2 = 4 cm;
s =\( \frac{perimeter of \triangle PQR}{2} = \frac{4 + 4 + 4}{2} \)= 6 cm;
Area of \(\triangle PQR\) by Heron's formula : \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}=\sqrt{6(6-4)(6-4)(6-4)}=4\sqrt3\) \(cm^2\)
42)In the given figure, if \( DE \parallel BC \), AD = 2.5 cm, DB = 3.5 cm and EC = 4.2 cm, then the measure of AC is:
SSC CGL 2020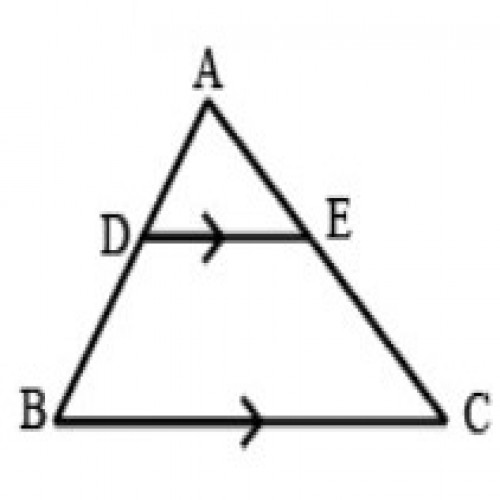
7.2 cm
Let AE = x; \( DE \parallel BC \) \(\therefore \angle ADE= \angle ABC; \space \angle AED = \angle ACB\); By AA - similarity theorem, \(\triangle ADE\sim \triangle ABC\) ; \(\therefore{AD\over AB}={AE\over AC}\) ; ⇒ \({2.5\over2.5+3.5}={x\over x+4.2}\) ; ⇒ x = 3 = AE; \(\therefore\) AC = AE + EC = 3 + 4.2 = 7.2 cm
SSC CGL 202043)If angles of a triangle are in the ratio of 2 : 3 : 4, then the measure of the smallest angle is:
\(40^0\)
Let angles of triangle be 2k, 3k and 4k.
\(\therefore 2k+3k+4k=180^0\) ; ⇒ \( k =\) \(20^0\) ;
Value of smallest angle = 2k = \(2\times20^0=40^0\)
SSC CGL 201644)The centroid of a triangle is the point where
the medians meet
SSC CGL 201645)In a triangle PQR, the side QR is extended to S. ∠QPR = 72° and ∠PRS = 110°, then the value of ∠PQR is:
38°
SSC CGL 201646)In ΔABC, ∠B = 70°and ∠C = 60°. The internal bisectors of the two smallest angles of ΔABC meet at O. The angle so formed at O is
125°
SSC CGL 202047)In \(\triangle ABC\), \(\angle B=90^0\). If the points D and E are on the side BC such that BD = DE = EC, then which of the following is true?
\(8AE^2 = 3AC^2 + 5AD^2\)
In \(\triangle ABE,\) ⇒ \(AE^2=AB^2+BE^2\) ____(i)
In \(\triangle ABD,\) ⇒ \(AD^2=AB^2+BD^2\) ____(ii)
In \(\triangle ABC,\) ⇒ \(AC^2=AB^2+BC^2\) ____(iii)
\(\therefore AE^2=AB^2+(2BD)^2\) ⇒ \(AE^2=AB^2+4BD^2\) ⇒ \(AE^2=AD^2+3BD^2\) ___(iv)
From equation (i)and (iii), \(BD^2 ={1\over5}(AC^2-AE^2)\) ____(v)
From equation (iv), \(AE^2=AD^2+{3\over5}(AC^2-AE^2)\) ⇒ \(8AE^2=5AD^2+3AC^2\)
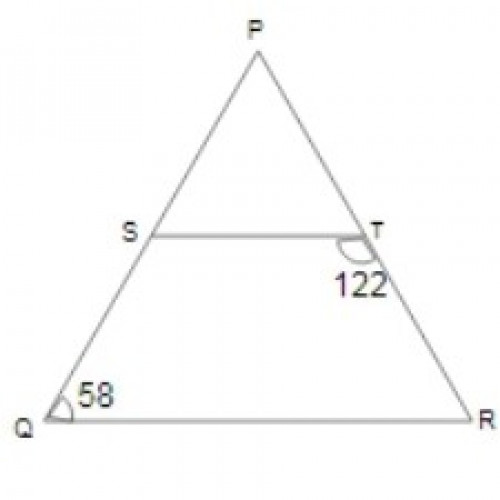
SSC CGL 202048)In \(\triangle PQR\), PQ = 24 cm. and \(\angle Q = 58^\circ\). S and T are the points on the sides PQ and PR, respectively, such that \(\angle STR = 122^\circ\). If PS = 14 cm and PT = 12 cm, then the length of RT is :
16 cm
\(\angle PTS + \angle STR = 180^0\) ;
\(\angle PTS = 180 - 122 = 58^0\) ;
\(\angle P\) is a common angle.
\(\triangle PQR\) and\( \triangle PTS\) are similar triangle. SO,
\(\frac{PT}{PQ} = \frac{PS}{PR}\) ; ⇒ \(\frac{12}{24} = \frac{14}{PR}\) ; ⇒ PR = 28 cm ;
RT = PR - PT = 28 - 12 = 16 cm
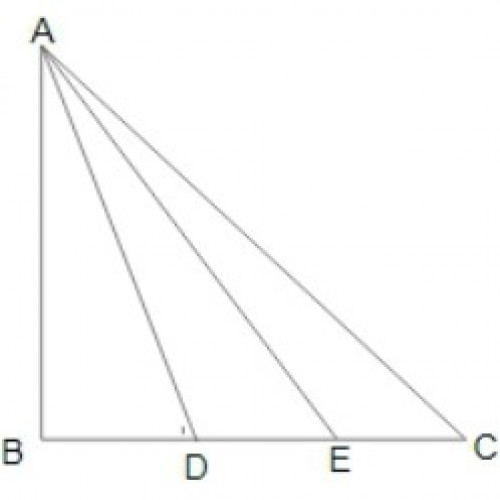
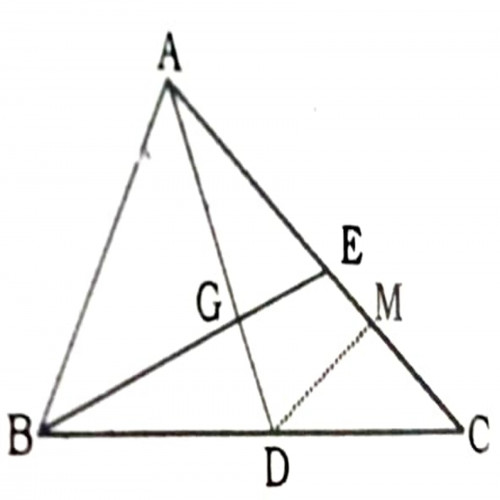
SSC CGL 202049)D is the midpoint of side BC of \(\triangle ABC\). Point E lies on AC such that \(CE={1\over3}AC\). BE and AD intersect at G. What is \(AG\over GD\) ?
4 : 1
CE = \({AC\over 3} \) and D is the midpoint of BC. Let, M be the midpoint of EC. [\(\therefore DM\parallel BE \) ⇒ \(DM\parallel GE\)]
In \(\triangle ADM\), to apply basic proportionality theorem , \(AE= {2AC\over 3}; \space EC= {AC\over3}\) ; \(EM= {1\over2}\times{AC\over3}= {AC\over6}\) ;
\(\therefore {AG\over GD}= {AE\over EM}= {2AC\over3}\div{AC\over6}\) = 4 : 1
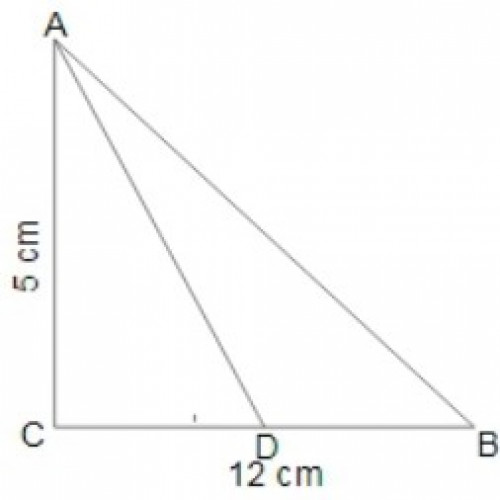
SSC CGL 202050)In \(\triangle ABC\), \(\angle C = 90^\circ\), AC = 5 cm and BC = 12 cm. The bisector of \( \angle A \) meets BC at D. What is the length of AD ?
\(\frac{5\sqrt{13}}{3}\) cm
By the Pythagoras theorem,
\((AB)^2 = (AC)^2 + (BC)^2\); ⇒ \((AB)^2 = (5)^2 + (12)^2\);
⇒ AB = 13 cm;
By angle bisector theorem,
\(\frac{AB}{BD} = \frac{AC}{CD}\);
Let CD be x cm.
\(\frac{13}{12 - x} = \frac{5}{x};\)
⇒ x = 60/18 = 10/3;
In \(\triangle ACD\),
\((AD)^2 = (AC)^2 + (CD)^2;\)
⇒ \((AD)^2 = (5)^2 + (\frac{10}{3})^2\); ⇒ AD = \(\frac{5\sqrt13}{3}\)